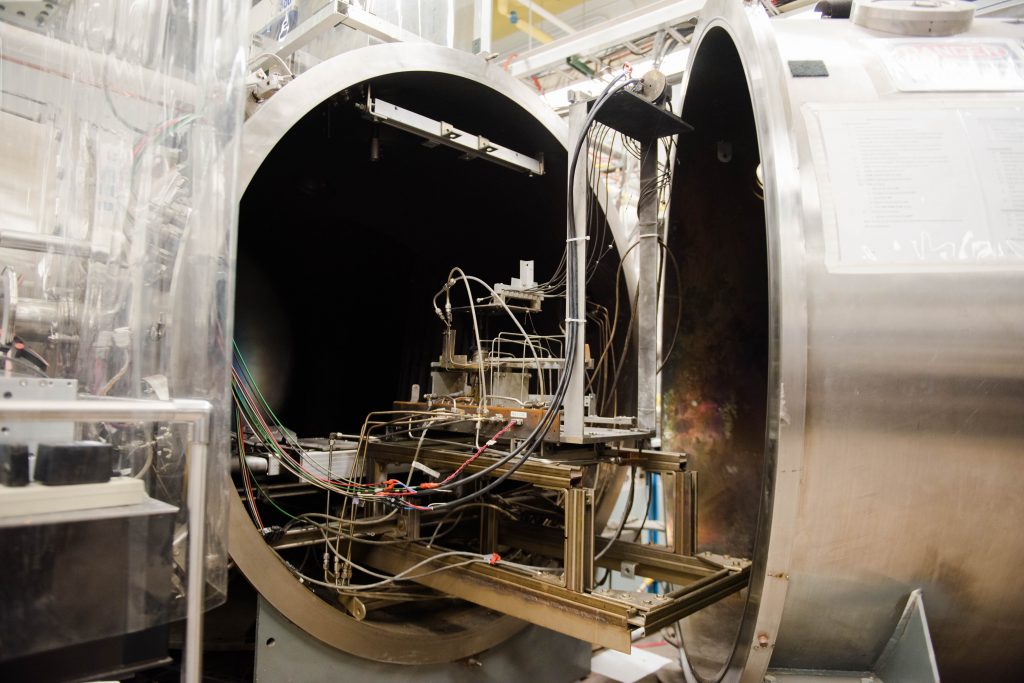
Xenon/Krypton Facility
The Xenon/Krypton facility is a 2-meter-diameter by 4-meter-long space simulation chamber for ground-testing flight-scale ion propulsion systems. The chamber is evacuated to ultimate pressure using two 48-inch diameter liquid nitrogen-assisted liquid helium cryogenic vacuum pumps. The vacuum facility is capable of testing thrusters up to 2 kW.
With the cryopumps the chamber can achieve a vacuum better than 1E-6 Torr (equivalent to 0.000000001 atmosphere or comparable to the space shuttle environment) and remove propellant gas emitted by the thruster at a speed of 120,000 L/s. The facility also utilizes a mechanical vacuum pump to back the cryopump.
The facility is equipped with a NASA-Glenn-style inverted pendulum thrust measurement stand, a dedicated gaseous mass flow control system for propellant supply, cooling water, power supplies and a comprehensive computer controlled data acquisition system. With the available diagnostics, thruster parameters such as thrust, specific impulse, electrical efficiency, and discharge oscillation can be readily measured.
In order to study the plasma flowfield and plume structure emitted from thrusters, a remotely controlled diagnostic manipulation system is fully contained within the vacuum chamber. The system is capable of 1-m by 1.5-m linear translation on two axes as well as rotation for motion control of assets during testing.
The existing laboratory instrumentation is available to the Condensable Propellant Facility as well.
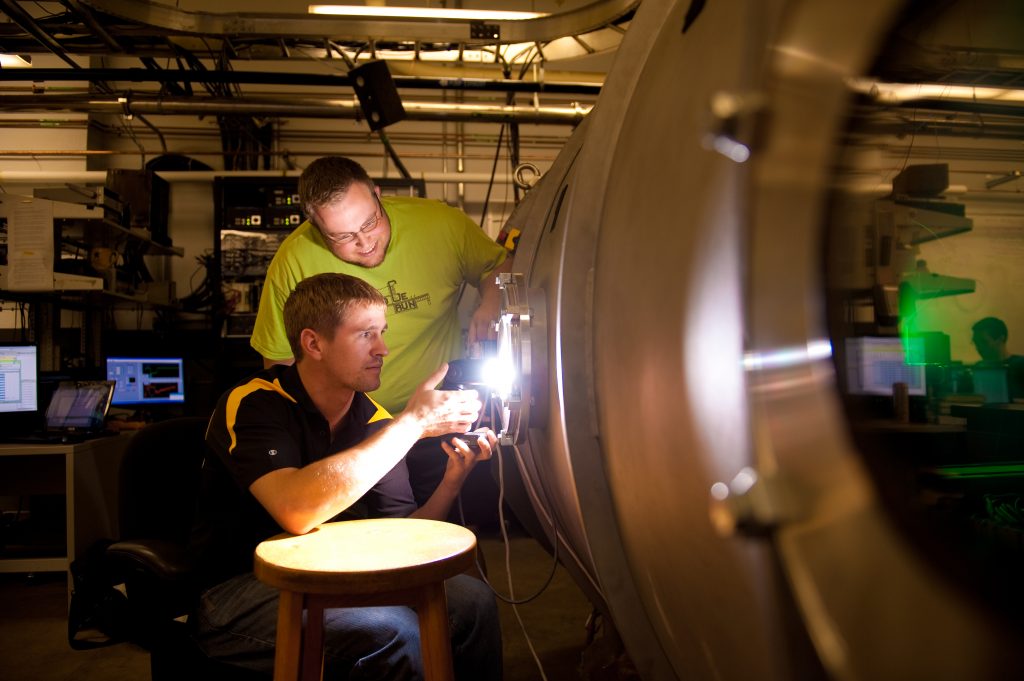

Condensable Propellant Facility
The compressible propellant ground test facility is specifically designed to evaluate EP thrusters operating on condensable propellants such as iodine, magnesium, bismuth, and zinc.
The 2-m-diameter by 4-m-long vacuum chamber utilizes three magnetically levitated turbomolecular pumps with pumping speeds of 2,000 L/s each for a robust, oil-free space environment simulation. The facility is capable of operating thrusters with power levels up to 20 kW.
In order to study the plasma flowfield and plume structure emitted from thrusters, a remotely controlled diagnostic manipulation system is fully contained within the vacuum chamber. The system is capable of 1-m by 1.5-m linear translation on two axes as well as rotation for motion control of assets during testing
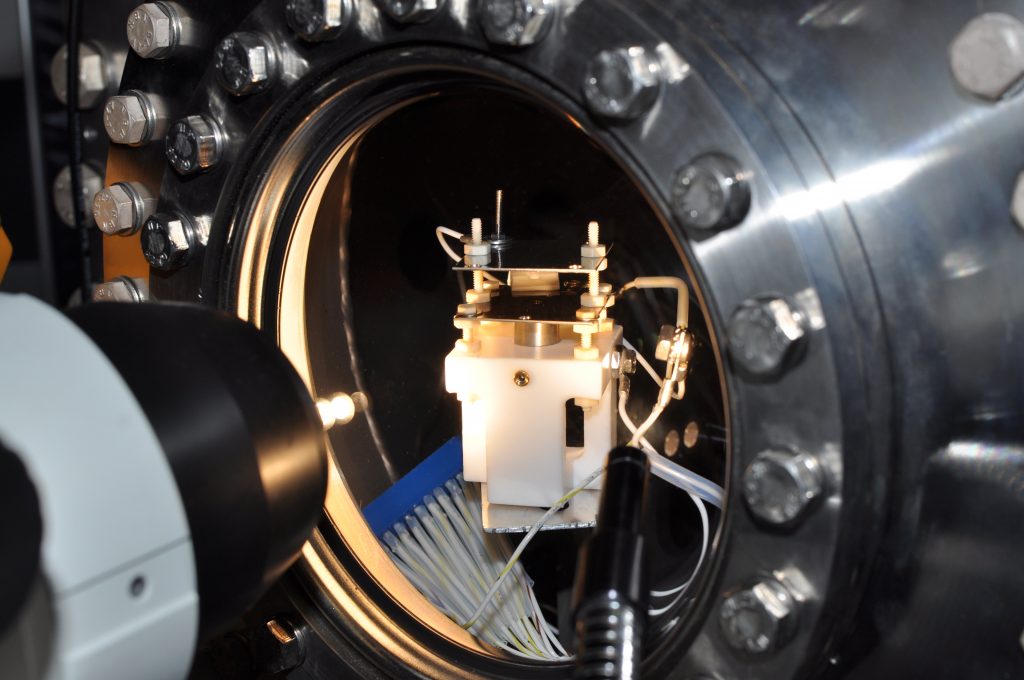
Micropropulsion Facility 1 (Ultra-High Vacuum)
Micropropulsion Facility 1 is a 0.5-meter -diameter by 0.5-meter-long stainless-steel chamber capable of pressures as low as 1×10-11 Torr.
The chamber is evacuated using a single 300 L/s magnetically levitated turbomolecular pump that is backed by a 110 L/min dry scroll pump. The tank is also equipped with a 300 L/s ion-sublimation combination pump to reach ultra-high vacuum.
An additional component to the UHV facility is a trinocular stereo microscope. The microscope has an optical magnification up to 90x and is equipped with a color digital camera. The camera provides the ability to perform in situ imaging, as well as the ability to record video directly through USB2.0.
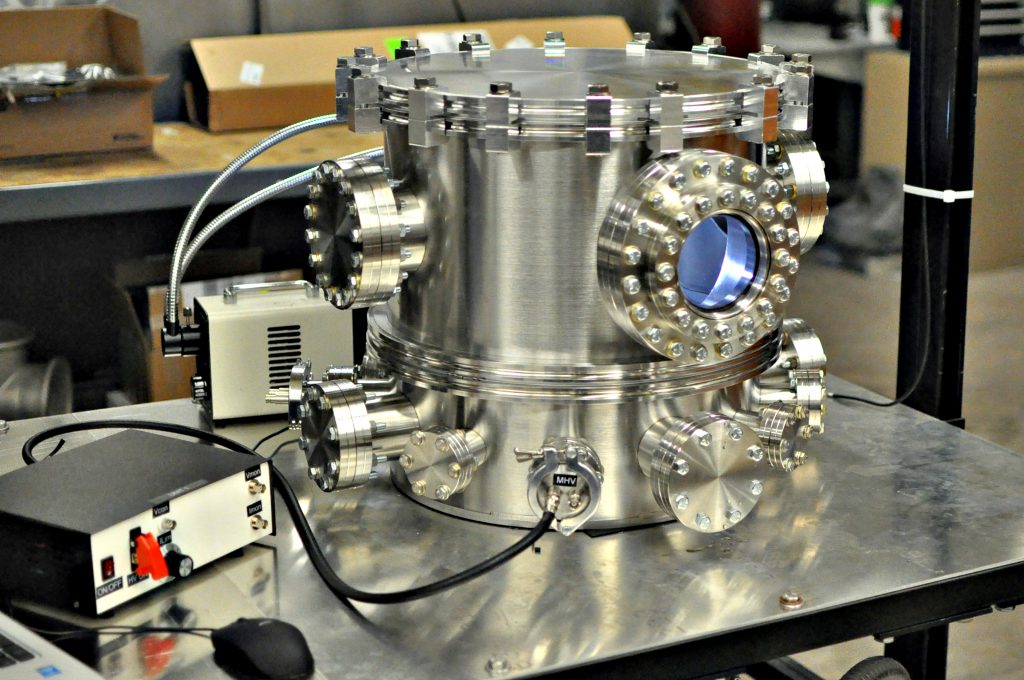

Micropropulsion Facility 2
Micropropulsion Facility 2 is a cylindrical chamber with a diameter of 42 cm and a height of 40 cm. This facility is evacuated using a 280 L/s turbomolecular pump that is backed by a 250 L/min triscroll pump.
Multiple viewports incorporated into the design of this facility enables high magnification imaging of thrusters and ion sources during vacuum testing.
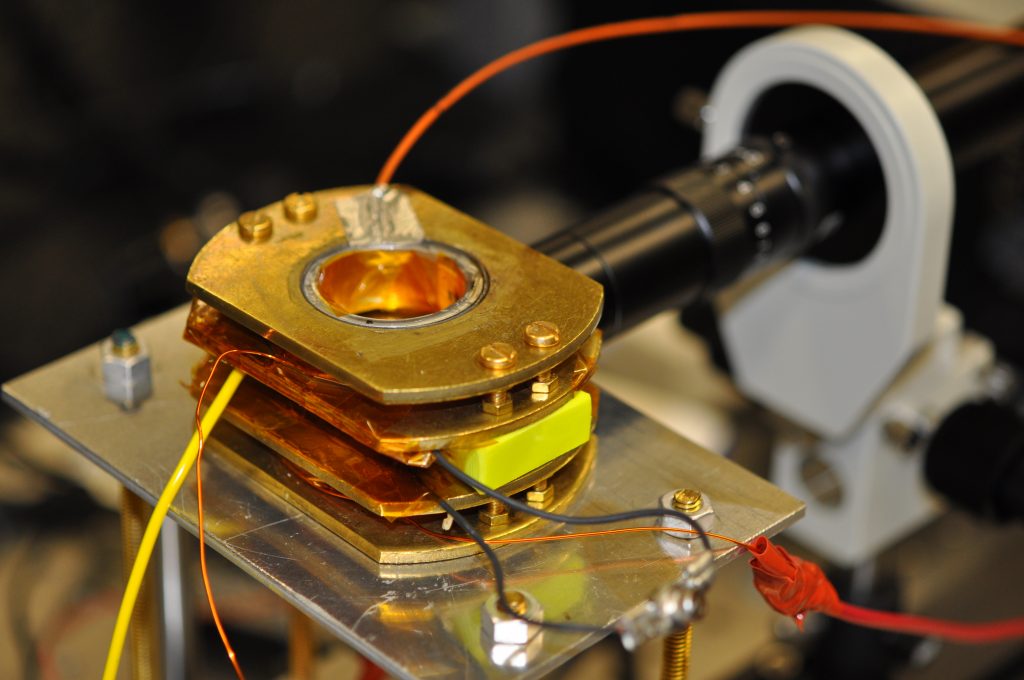
High Magnification Imaging Setup
This setup consists of a 2.5-10x variable zoom imaging lens, a collimated 472-nm (blue) light source, and a 5-megapixel USB 3.0 camera. The integrated setup has a field-of-view of view ranging from 2.24×1.68 mm to 0.56×0.42 mm. The resolution of this imaging setup and obtainable silhouette images makes this system ideal for observing and detecting meniscus profiles of electrospray emission sources.
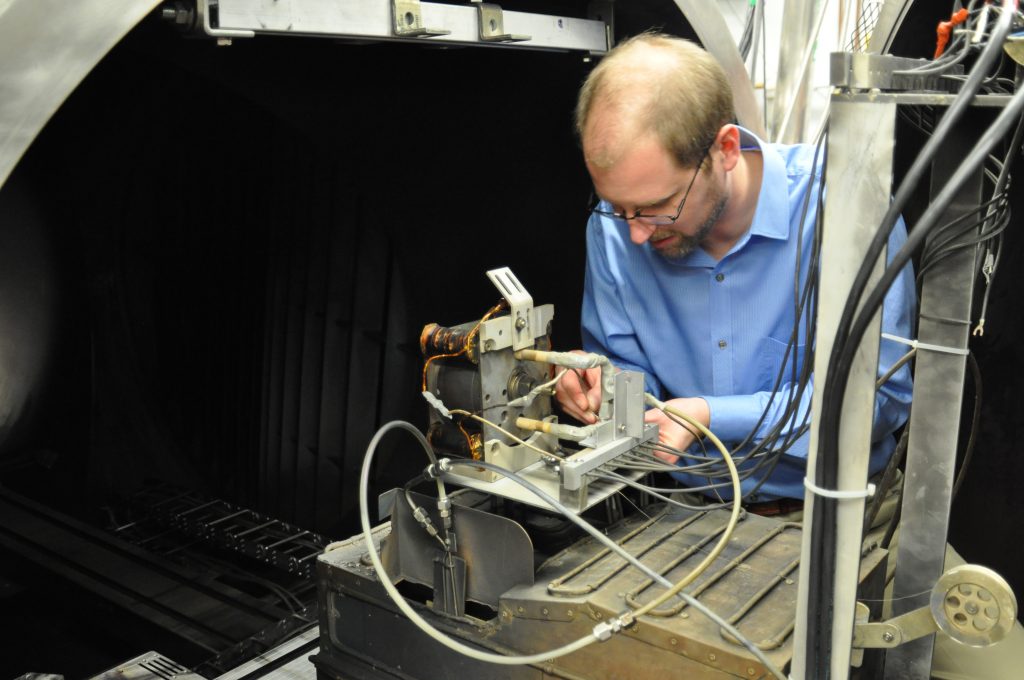

Milli-Newton Thrust Stand
The milli-newton thrust stand is an inverted-pendulum, null-displacement thrust stand based on the NASA-Glenn design. Thrust from the attached propulsion source attempts to displace the inverted pendulum. Thrust stand displacement is measured by a linear voltage displacement transducer (LVDT). This displacement is “nulled” by an onboard electromagnet which provides a restoring force, the current of which is directly proportional to the thrust.
The thrust stand is capable of resolving thrust as small as 1mN [simple_tooltip content=’Hopkins, Mark A., Evaluation of Magnesium as a Hall Thruster Propellant, Doctoral Dissertation, Department of Mechanical Engineering-Engineering Mechanics, Michigan Technological University, 2014.’][Hopkins][/simple_tooltip], with an estimated experimental uncertainty of ±5% [simple_tooltip content=’Massey, Dean R., Development of a Direct Evaporation Bismuth Hall Thruster, Doctoral Dissertation, Department of Mechanical Engineering-Engineering Mechanics, Michigan Technological University, 2008.’][Massey][/simple_tooltip]. The thrust stand is capable of being calibrated at vacuum to minimize thermal drift and temporal variation in output.
Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometer
The TOF spectrometer is a unique and custom instrument dedicated to electrospray propulsion research. The device combines an electrostatic energy analyzer with a TOF mass-to-charge detector to provide full energy and mass spectral diagnostics of electrospray beams. The beam line includes a retarding potential analyzer (RPA), quartz crystal microbalance (QCM), and faraday probe all mounted on a rotation stage, enabling different sensors to be utilized in quick succession without needing to halt emission.
This facility has a base pressure of 1×10-8 Torr and utilizes a 250 L/s turbomolecular pump backed by a 100 L/s dry scroll pump.
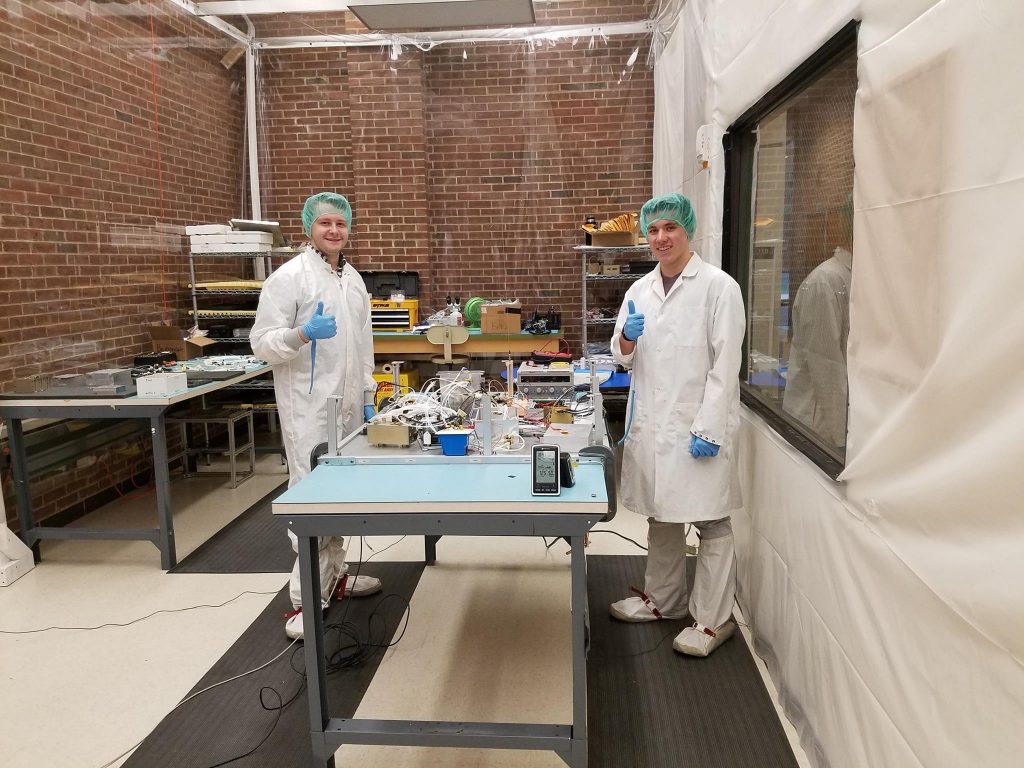

Spacecraft Clean Assembly Area
The enterprise maintains a class 100,000 clean room on campus for development and testing of flight hardware.

